INTERNATIONAL CONVENTION FOR THE SAFETY OF LIFE AT SEA (SOLAS) 1974
The SOLAS Convention in its successive forms is generally regarded as the most important of all international treaties concerning the safety of merchant ships. The first version was adopted in 1914, in response to the Titanic disaster, the second in 1929, the third in 1948, and the fourth in 1960. The 1974 version includes the tacit acceptance procedure - which provides that an amendment shall enter into force on a specified date unless, before that date, objections to the amendment are received from an agreed number of Parties.
Technical provisions
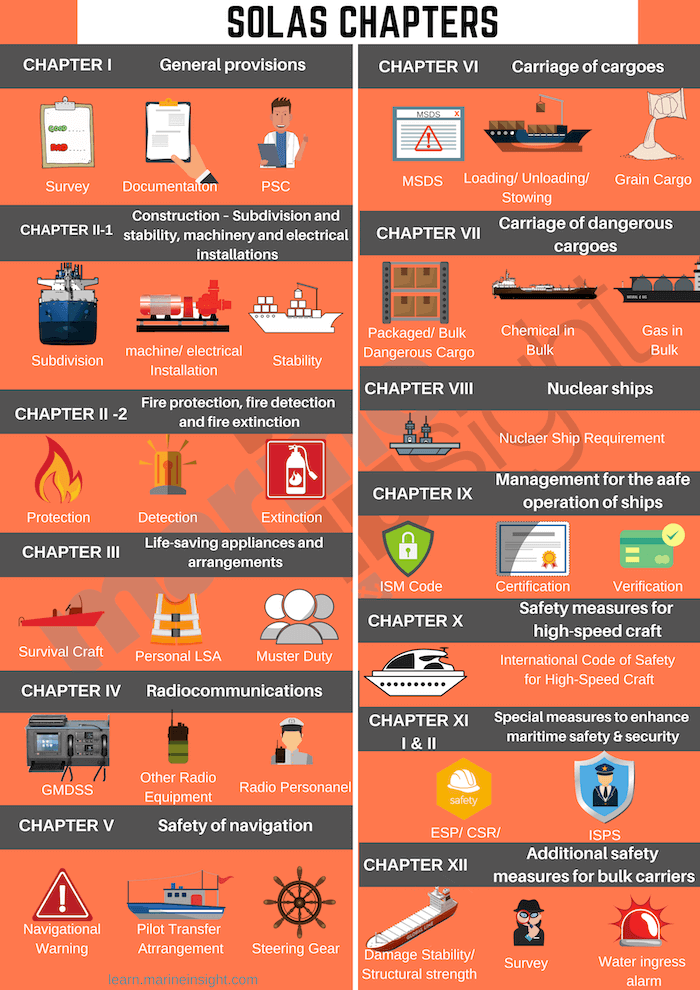
The main objective of the SOLAS Convention is to specify minimum standards for the construction, equipment and operation of ships, compatible with their safety. Flag States are responsible for ensuring that ships under their flag comply with its requirements, and a number of certificates are prescribed in the Convention as proof that this has been done. Control provisions also allow Contracting Governments to inspect ships of other Contracting States if there are clear grounds for believing that the ship and its equipment do not substantially comply with the requirements of the Convention - this procedure is known as port State control. The current SOLAS Convention includes Articles setting out general obligations, amendment procedure and so on, followed by an Annex divided into 14 Chapters.
Includes regulations concerning the survey of the various types of ships and the issuing of documents signifying that the ship meets the requirements of the Convention. The Chapter also includes provisions for the control of ships in ports of other Contracting Governments.
Chapter II-1 - Construction - Subdivision and stability, machinery and electrical installations
The subdivision of passenger ships into watertight compartments must be such that after assumed damage to the ship's hull the vessel will remain afloat and stable. Requirements for watertight integrity and bilge pumping arrangements for passenger ships are also laid down as well as stability requirements for both passenger and cargo ships.
Chapter II-2 - Fire protection, fire detection and fire extinction
Includes detailed fire safety provisions for all ships and specific measures for passenger ships, cargo ships and tankers.
Chapter III - Life-saving appliances and arrangements
The Chapter includes requirements for life-saving appliances and arrangements, including requirements for life boats, rescue boats and life jackets according to type of ship. The International Life-Saving Appliance (LSA) Code gives specific technical requirements for LSAs and is mandatory under Regulation 34, which states that all life-saving appliances and arrangements shall comply with the applicable requirements of the LSA Code.

Chapter IV - Radiocommunications
The Chapter incorporates the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS). All passenger ships and all cargo ships of 300 gross tonnage and upwards on international voyages are required to carry equipment designed to improve the chances of rescue following an accident, including satellite emergency position indicating radio beacons (EPIRBs) and search and rescue transponders (SARTs) for the location of the ship or survival craft.
Chapter V - Safety of navigation
Chapter V identifies certain navigation safety services which should be provided by Contracting Governments and sets forth provisions of an operational nature applicable in general to all ships on all voyages. This is in contrast to the Convention as a whole, which only applies to certain classes of ship engaged on international voyages.
Chapter VI - Carriage of Cargoes
The Chapter covers all types of cargo (except liquids and gases in bulk) "which, owing to their particular hazards to ships or persons on board, may require special precautions". The regulations include requirements for stowage and securing of cargo or cargo units (such as containers). The Chapter requires cargo ships carrying grain to comply with the International Grain Code.

The regulations are contained in three parts:
Chapter VIII - Nuclear ships
Gives basic requirements for nuclear-powered ships and is particularly concerned with radiation hazards. It refers to detailed and comprehensive Code of Safety for Nuclear Merchant Ships which was adopted by the IMO Assembly in 1981.
The Chapter makes mandatory the International Safety Management (ISM) Code, which requires a safety management system to be established by the shipowner or any person who has assumed responsibility for the ship (the "Company").
The Chapter makes mandatory the International Code of Safety for High-Speed Craft (HSC Code).
The Chapter clarifies requirements relating to authorization of recognized organizations (responsible for carrying out surveys and inspections on Administrations' behalves); enhanced surveys; ship identification number scheme; and port State control on operational requirements.
Chapter XI-2 - Special measures to enhance maritime security
Regulation XI-2/3 of the chapter enshrines the International Ship and Port Facilities Security Code (ISPS Code). Part A of the Code is mandatory and part B contains guidance as to how best to comply with the mandatory requirements. Regulation XI-2/8 confirms the role of the Master in exercising his professional judgement over decisions necessary to maintain the security of the ship. It says he shall not be constrained by the Company, the charterer or any other person in this respect.
Chapter XII - Additional safety measures for bulk carriers
The Chapter includes structural requirements for bulk carriers over 150 metres in length.
Makes mandatory from 1 January 2016 the IMO Member State Audit Scheme.
Chapter XIV - Safety measures for ships operating in polar waters
The chapter makes mandatory, from 1 January 2017, the Introduction and part I-A of the International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters (the Polar Code).

Comments
Post a Comment